题目
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
1
2
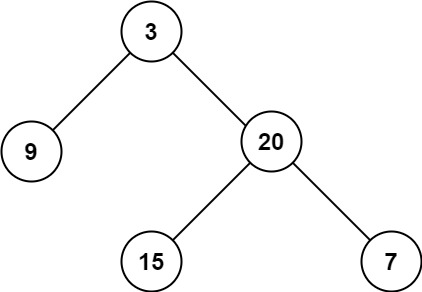
| 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
|
示例 2:
1
2
| 输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
|
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 104] 区间内。
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
实现代码
通过二叉树的递归遍历(DFS)实现
方式一
前序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
class Solution {
int max = 0, n = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return max;
}
traverse(root);
return max;
}
public void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
n++;
max = Math.max(max, n);
maxDepth(root.left);
maxDepth(root.right);
n--;
}
}
|
方式二
后序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftMaxDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightMaxDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return 1 + Math.max(leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth);
}
|
时间复杂度
因为会走完所有节点,所以为O(N)
空间复杂度
递归遍历所占的额外空间就是占用的栈帧内存,取决于数的高度h,平均情况下是O(logN),最坏情况下数呈现链状,为O(N),所以空间复杂度是O(h)