题目
实现一个优先级队列(二叉堆)
实现代码
通过完全二叉树来实现,并且底层使用数组来构建完全二叉树的逻辑结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
|
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
static class PriorityQueue {
private final int[] arr;
private int size;
public PriorityQueue(int capacity) {
arr = new int[capacity + 1];
size = 0;
}
public int left(int node) {
return node * 2;
}
public int right(int node) {
return node * 2 + 1;
}
public int parent(int node) {
return node / 2;
}
public void sink(int node) {
int min = node;
while (left(node) <= size || right(node) <= size) {
if (left(node) <= size && arr[left(node)] < arr[min]) {
min = left(node);
}
if (right(node) <= size && arr[right(node)] < arr[min]) {
min = right(node);
}
if (min == node) {
return;
}
int tmp = arr[node];
arr[node] = arr[min];
arr[min] = tmp;
node = min;
}
}
public void rise(int node) {
while (node > 1 && arr[parent(node)] > arr[node]) {
int tmp = arr[node];
arr[node] = arr[parent(node)];
arr[parent(node)] = tmp;
node = parent(node);
}
}
public void push(int val) {
arr[size + 1] = val;
rise(size + 1);
size++;
}
public int pop() {
int tmp = arr[1];
arr[1] = arr[size];
size--;
sink(1);
return tmp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(5);
queue.push(3);
queue.push(2);
queue.push(1);
queue.push(5);
queue.push(4);
System.out.println(queue.pop());
System.out.println(queue.pop());
System.out.println(queue.pop());
System.out.println(queue.pop());
System.out.println(queue.pop());
}
}
|
数组构建完全二叉树的原理
优先级队列(二叉堆)的定义:
树结构的任意节点的值都必须大于或等于小于其左右子数所有节点的值;
完全二叉树的定义:
每一层节点都是紧凑靠左排列的,并且除了最后一层,其他层都是满的,如下图:
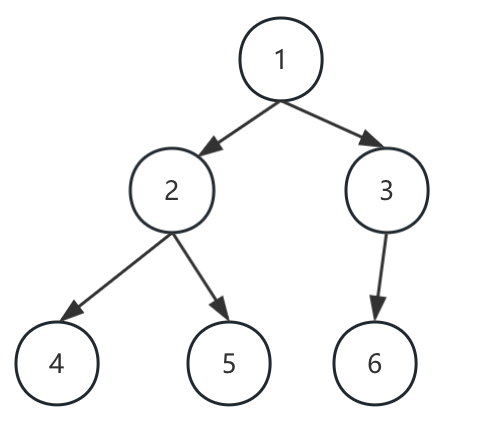
那么,使用数组进行构建则如下:
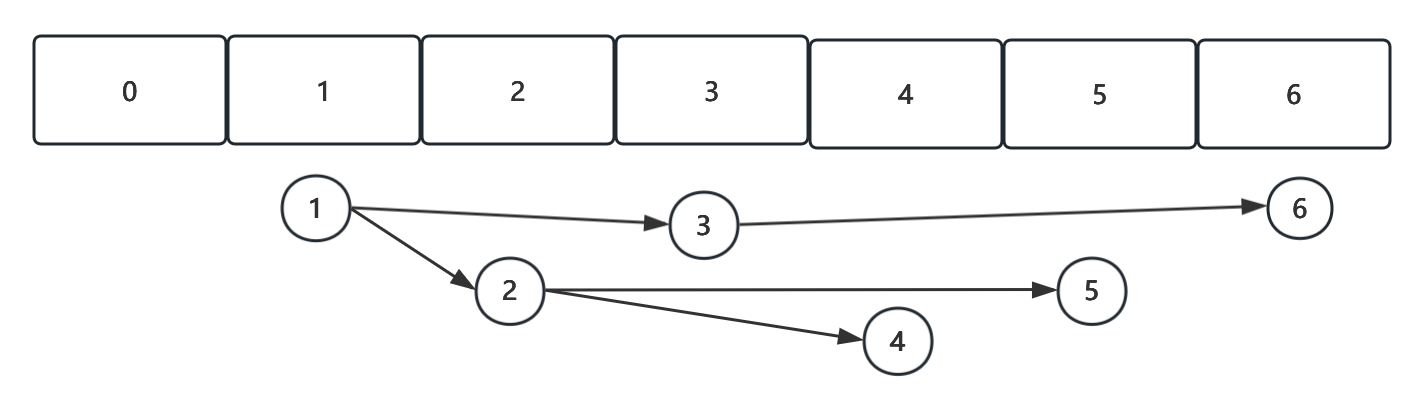
会发现以下规律:
- 左节点索引是当前节点索引值的2倍;
- 右节点索引是当前节点索引值的2倍加1;
- 父节点是当前节点索引值除于2的商;
基于以上数组实现完全二叉树逻辑结构的规律,只要在其基础上维护好优先级队列的特性,就很容易实现一个优先级队列的数据结构;